How is OEE calculated?
OEE is calculated as a percentage based on three core factors: Availability, Performance, and Quality.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a key performance indicator (KPI) used in manufacturing to measure the efficiency and effectiveness of equipment. It provides a standardized method for evaluating how well a production process is running compared to its full potential. By identifying and reducing inefficiencies, OEE helps manufacturers optimize productivity, minimize downtime, and improve overall operational performance.
OEE Calculation:
OEE = Availability × Performance × Quality
-
Availability:
Availability measures the percentage of scheduled production time that the equipment is actually running. It accounts for unplanned stops, such as breakdowns and changeovers.

-
- Operating Time: Planned Production Time - Downtime events (e.g., breakdowns, adjustments, changeovers).
- Planned Production Time: Total time scheduled for production
-
Performance:
Performance evaluates whether the equipment is running at its optimal speed. It considers speed losses due to minor stops or running below maximum capacity.

- Ideal Cycle Time: The theoretical minimum time required to produce one unit.
- Total Count: The total number of units produced during Operating Time.
If the machine runs slower than its ideal speed, Performance decreases.
-
Quality:
Quality measures the percentage of good-quality products produced compared to the total number of products manufactured. It accounts for defects and rework.

- Good Count: Number of units produced that meet quality standards.
- Total Count: All units produced (including defects).
Interpreting OEE Scores:
After you have calculated Availability, Performance, and Quality (each expressed as a decimal), the OEE is:

- 100% OEE = Perfect production (no downtime, maximum speed, and zero defects)
- 85% OEE = World-class manufacturing performance
- 60% OEE = Typical for many manufacturers, with room for improvement
- Below 40% OEE = Significant inefficiencies that need immediate attention
Example:
-
Consider an 8-hour work shift (480 minutes), where:
- The machine experienced 60 minutes of downtime for maintenance, leaving 420 minutes of actual operating time.
- The ideal cycle time to produce one unit is 1 minute.
- Within the 420 minutes of operating time, the machine produced 350 units.
- Of these 350 units, 330 were of good quality.
Now, calculating the key OEE components:


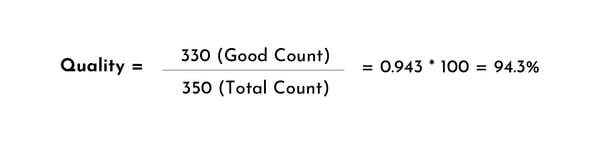
 This OEE score of approximately 69% indicates that the machine is operating at just under 70% efficiency. The result reflects a combination of downtime, slower-than-optimal production speed, and some quality losses. Identifying and addressing these factors can help improve overall equipment performance.
This OEE score of approximately 69% indicates that the machine is operating at just under 70% efficiency. The result reflects a combination of downtime, slower-than-optimal production speed, and some quality losses. Identifying and addressing these factors can help improve overall equipment performance.
